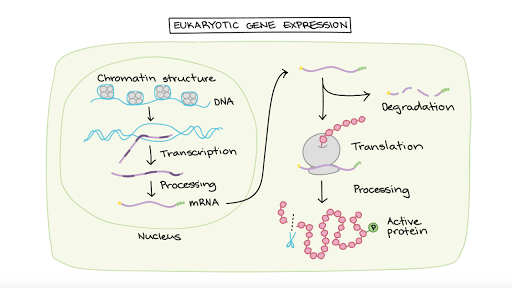
Which Molecules in Eukaryotic Cells Regulate Gene Expression
Repressors activators and inducers. What are the two main ways of controlling metabolism in bacterial cells.

Gene Regulation In Eukaryotes Biology Online Tutorial
It consists of four phases.
. Regulates the expression of the gene in different parts of the body at different times in the animals life cycle. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products protein or non-coding RNA and ultimately affect a phenotype as the final effectThese products are often proteins but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA tRNA and small nuclear RNA snRNA the product. The dynamic nature of polyA tails is therefore vital in regulating gene expression and is important in almost every aspect of eukaryotic biology.
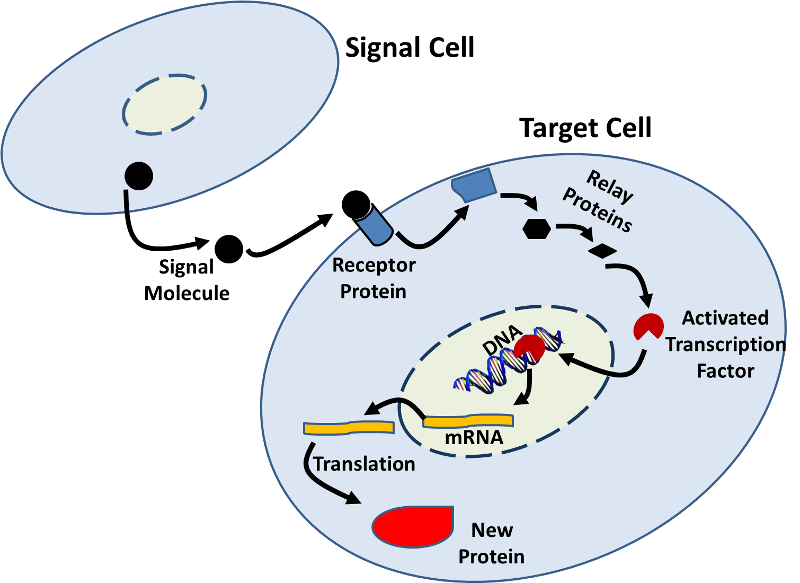
National Center for Biotechnology Information. The ability to regulate gene expression allows cells to deliver a functional protein whenever its needed for their normal functioning or survival. Both repressors and activators regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sites adjacent to the genes they control.
To avoid this it is necessary to regulate the expression of keratin gene. E coli regulate their gene expression to save or reserve resources when the environment is giving them what they need. Adjust activity of present.
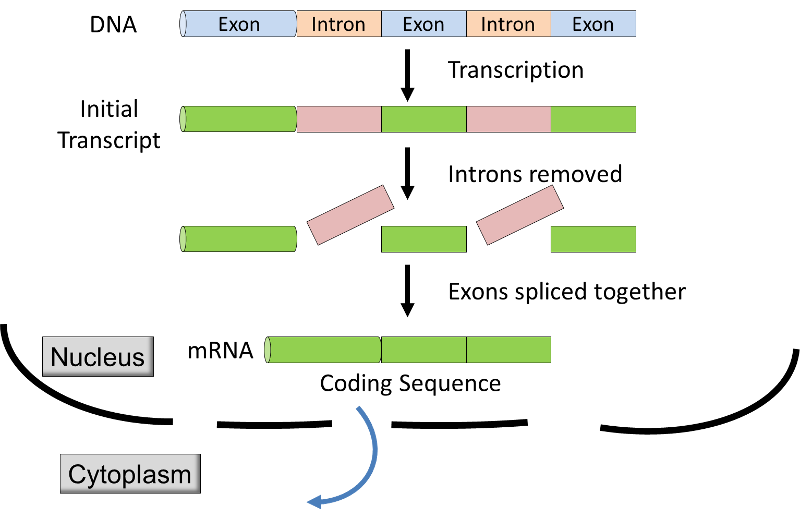
These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become the building blocks of. This complexity is in sharp contrast to the relatively simple process of gene expression in prokaryotic cells where the product of the gene is the mRNA and there is no nucleus that separates the genetic material from the machinery necessary to synthesize proteins. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription.
A single cell is often a complete organism in itself such as a bacterium or yeast. The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F complex which recognizes the 7-methylguanosine cap structure at the 5 end of messenger RNAs. Association of this protein with the 4F complex is the rate-limiting step in.
Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. Translation initiation is the process by which the ribosome and its associated factors bind an mRNA and are. This mechanism underlies various physiological and pathological processes including cellular adaptations to novel environments maintenance of homeostasis and recovery from damages.
Gene expression is regulated by factors both extrinsic and intrinsic to the cell. Each gene has within it a set of instructions for making molecules that organisms need. Cell-extrinsic factors that regulate expression include environmental cues such as small molecules secreted.
Repressors and activators are proteins produced in the cell. Gene translation elongation termination and recapping. Cell in biology the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed.
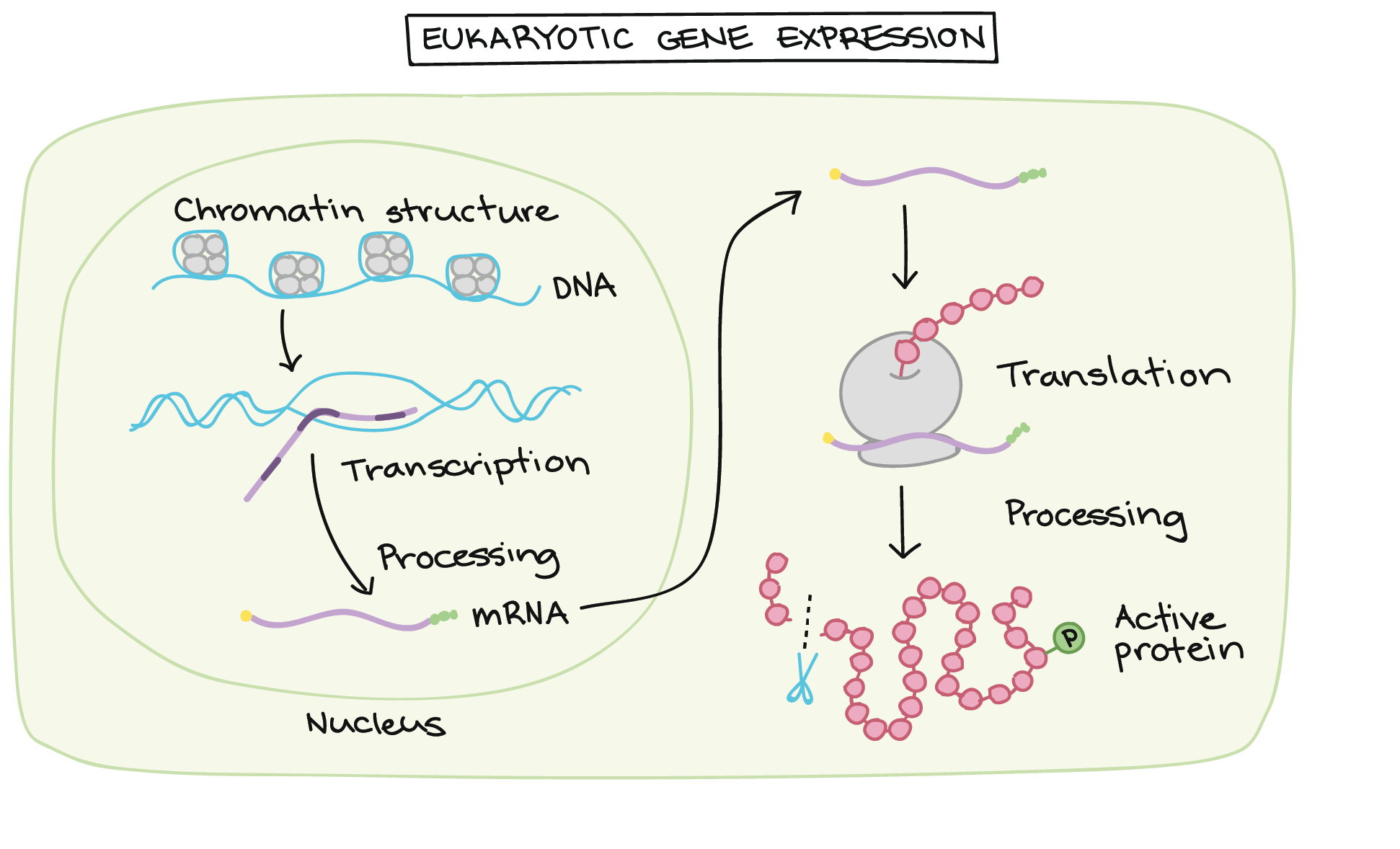
The presence of multiple switches enables the same gene to be used many times in different contexts and thus greatly expand the functional versatility of individual genes. Definition of Gene Expression. Regulation of gene expression includes different mechanisms through which our cells manage the amount of produced protein by our genes.
Mutations in regulatory switches affect expression of a particular gene in a particular tissue. 114 Thus in a bacterium protein synthesis actually begins on a nascent RNA molecule well before the. A gene is a small piece of genetic material written in a code and called DNA.
Eukaryotic translation is the biological process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in eukaryotes. In prokaryotic cells there are three types of regulatory molecules that can affect the expression of operons. The process of initiation of translation in eukaryotes.
The encoded protein aids in translation initiation by recruiting ribosomes to the 5-cap structure. Regulation of gene occurs differently depending on the type of organisms- prokaryotic or. E coli feed on tryptophan they produce it when tryptophan is low in their environment and they halt the production when it is abundant in their environment.
The ability to perform analysis of gene expression.
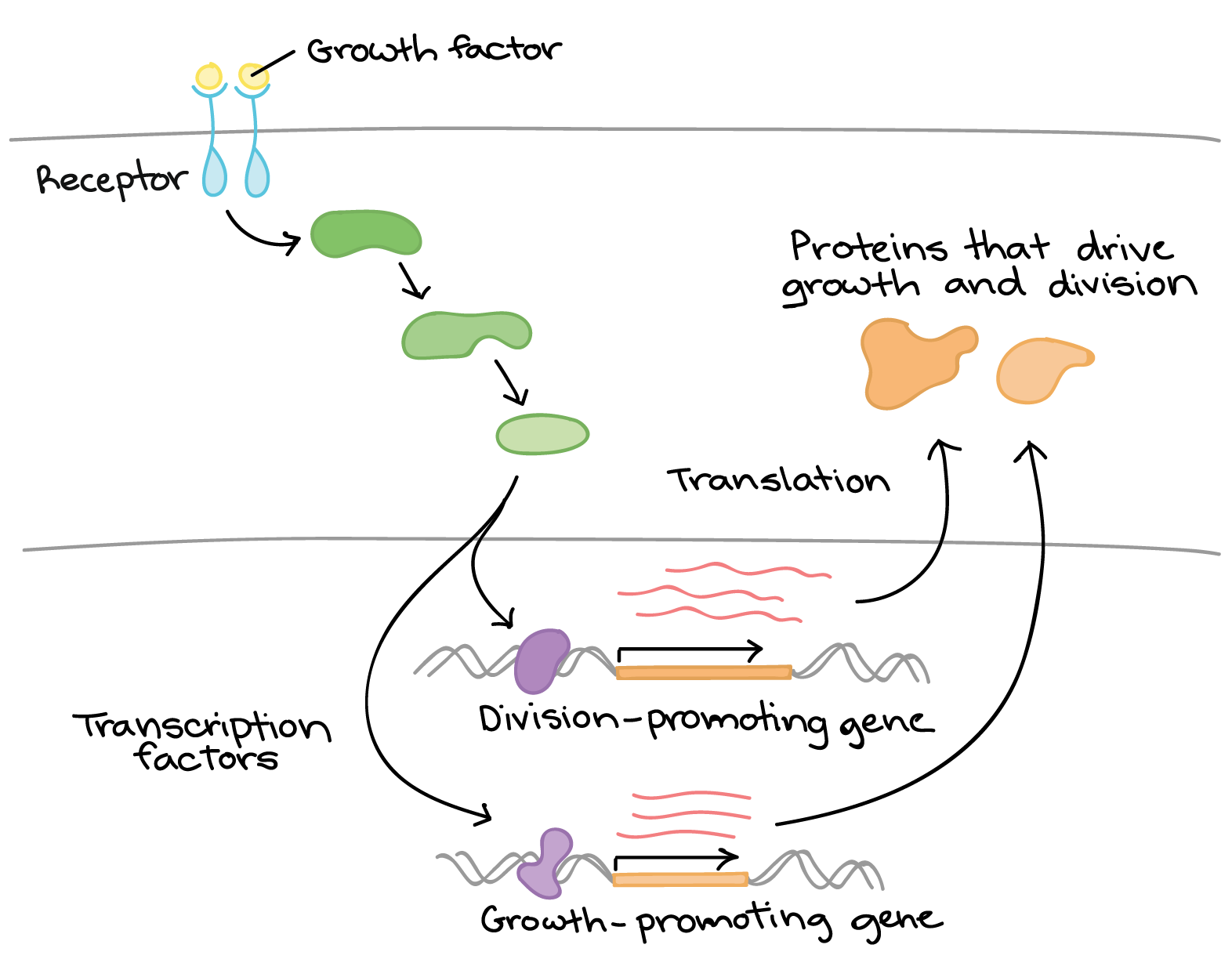
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
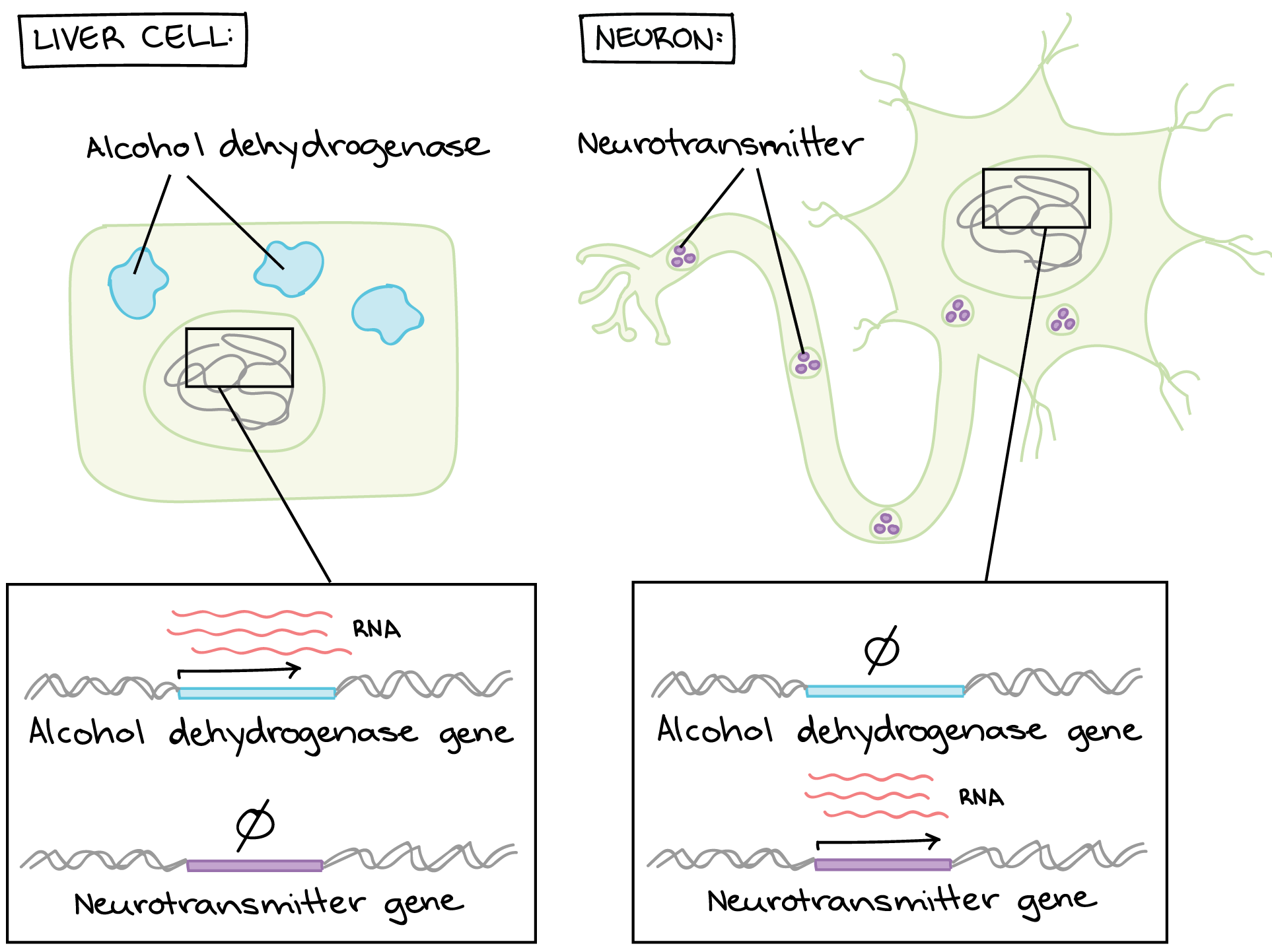
Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy

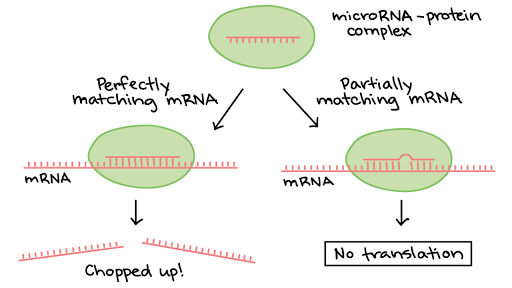
Regulation Of Gene Expression In Eukaryotes

Gene Expression Regulates Cell Differentiation Learn Science At Scitable
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
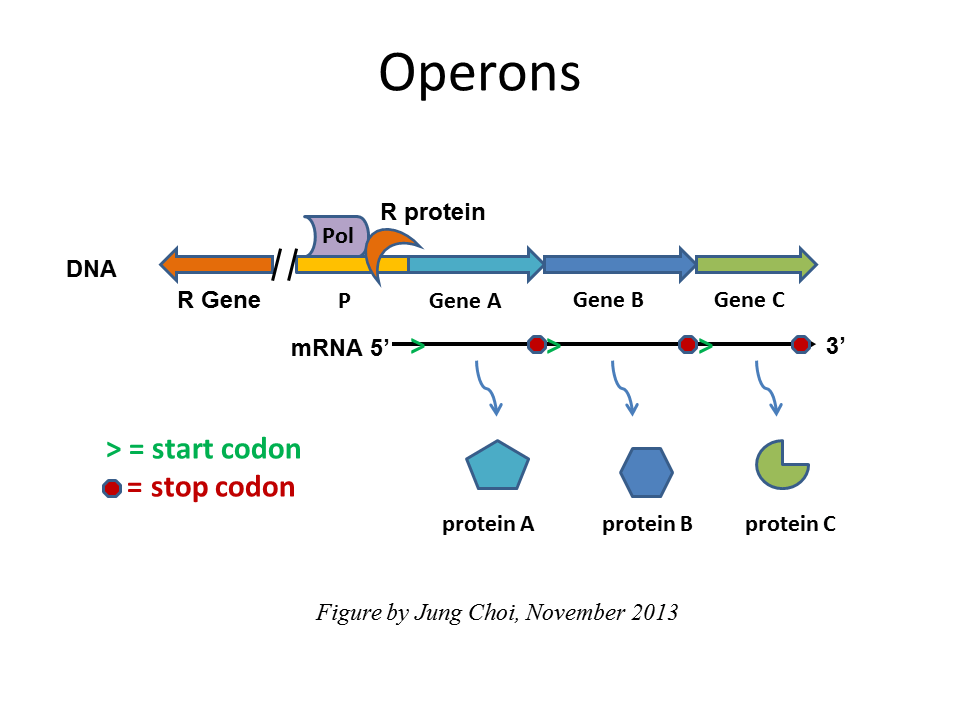
Gene Regulation Biological Principles

Regulation After Transcription Article Khan Academy
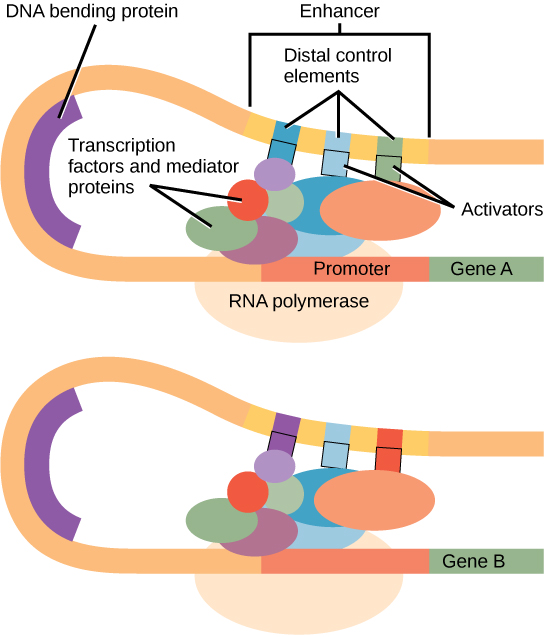
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Biology For Majors I

Pdf A Review On Regulation Of Gene In Eukaryotes

Quia Ap Chapter 19 Eukaryotic Genomes Detailed

Regulation Of Gene Expression Sciencedirect
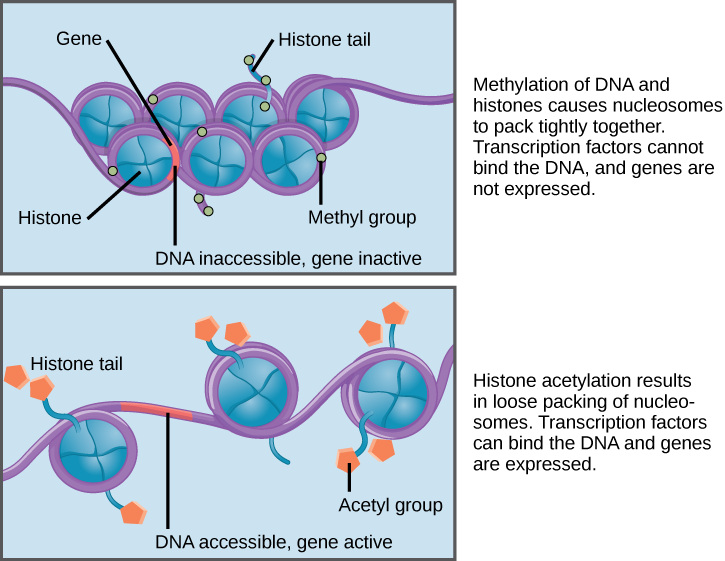
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Biology For Majors I

Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy

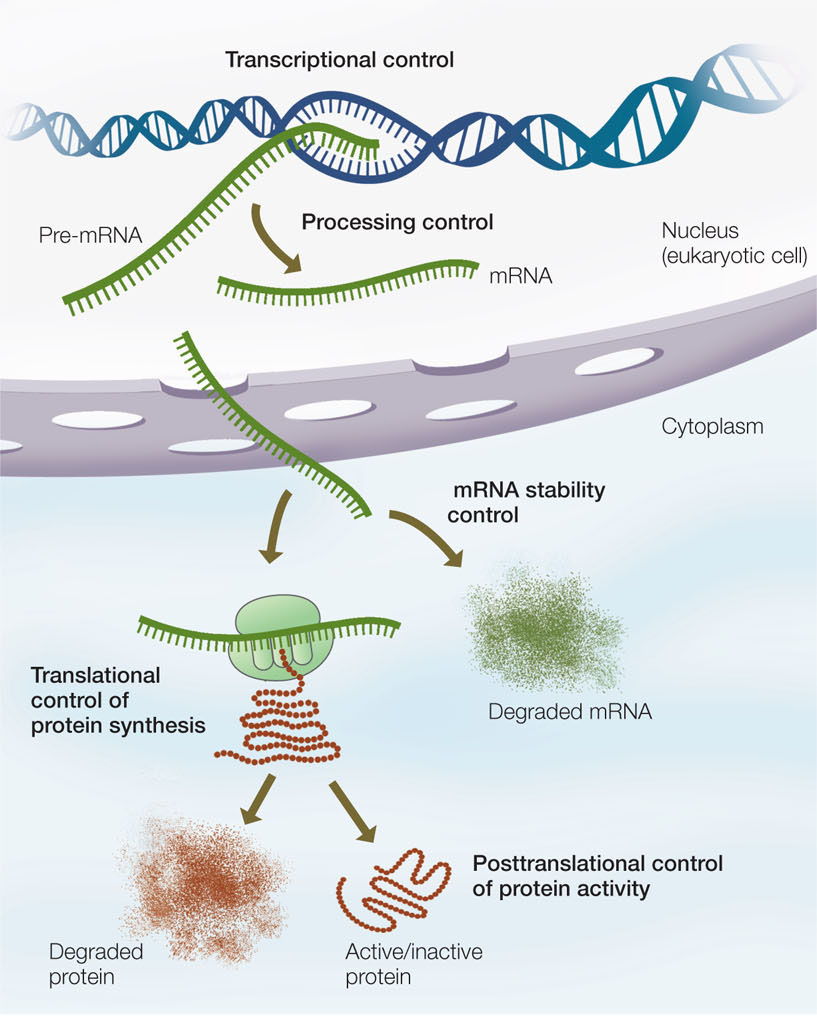
Comments
Post a Comment